Have you ever been confused by the parameter “display contrast ratio”? Contrast ratio is more than just a number in a technical specification, it directly determines how vivid and detailed the image you see is.
Whether it’s for office, entertainment or professional design, screen contrast ratio is a key factor in the visual experience. So what is contrast ratio? How does it affect the display? What is the difference between high contrast and low contrast? This article will provide you with all the answers to help you choose the most suitable LED display to enhance your visual enjoyment!
1.What is Display Contrast Ratio?
2.How to Test Contrast Ratio?
3.Why Does Contrast Ratio Matter in an LED Display?
4.Static Contrast Ratio vs Dynamic Contrast Ratio
5.Contrast Ratio of LED, LCD, OLED, QLED Displays
6.1000:1 vs 3000:1 vs 5000:1 LED Screen Contrast Ratio
7.What Factors Influence Screen Contrast Ratio?
8.How to Improve LED Display Contrast Ratio?
9.How to Choose the Best Contrast Ratio?
10.FAQs
11.Summary
1. What is Display Contrast Ratio?
Contrast ratio refers to the difference in brightness between the lightest (white) and darkest (black) elements that a display can produce. It’s an important metric for screens, including LED displays, as it impacts how vivid the colors appear and how clear the details are in both bright and dark scenes.
For example, a display with a contrast ratio of 2,000:1 means the brightest white is 2,000 times brighter than the darkest black the screen can show. The higher the contrast ratio, the deeper the blacks and the more vibrant the colors, leading to better overall image quality.

2. How to Test Contrast Ratio?
2.1 Formula for Contrast Ratio:
Contrast Ratio= Brightness of White/Brightness of Black
Note:
- Brightness of White is the maximum luminance of the white area, usually measured in nits (cd/m²).
- Brightness of Black is the minimum luminance of the black area, also measured in nits.
2.2 The Process of Testing Display Contrast Ratio:
- Set the LED display to a standard mode to ensure the brightness is in a fixed level.
- Use a test image or pattern that features both pure white and pure black areas.
- Test images that gradually transition from black to white.
- Use a light meter or a lux meter to measure the brightness of the brightest white area on the screen. Record the peak white value.
- Adopt the same method to test the darkest black value.
- Take note of the brightness values of both the maximum white brightness and darkest black value that should ideally be very close to 0 nits.
- Use the formula above to calculate the contrast ratio.

3. Why Does Contrast Ratio Matter in an LED Display?
The contrast ratio is crucial in an LED display because it directly affects the overall image quality and visual experience. Here are a few reasons why contrast ratio matters:
3.1 Enhanced Colour Vibrancy
LED displays can produce more vivid reds, greens and blues. This is especially important for displays that are used in advertising, media, or entertainment.
3.2 Increased Visual Clarity
A higher display contrast ratio, for example, allows the display, when displaying a video with bright highlights and dark shades, to show the finer details of the shadows without sacrificing the vibrant highlights. The result is a more detailed image.
3.3 Better Image Detail
The display’s ability to create deeper blacks and whiter contrasts can simulate the natural contrasts found in real world environments. This will make the viewing experience more immersive.
3.4 Essential for Professional Applications
A high display contrast ratio for professional LED displays is crucial in industries such as film production, digital signage and gaming. This allows professionals to judge the content accurately, and produces more precise and engaging images.
3.5 Enhances Readability Under Varying Lighting Conditions
A higher contrast ratio is required in environments that have changing ambient lighting, such as outdoor digital signage and LED billboards. This ensures the content remains legible even when bright sunlight or low light conditions are present.
3.6 Reduce Eye Strain
The LED displays with poor contrast ratios tend to make dark elements look washed out and bright elements overly harsh. This can cause eye strain, especially when viewing content for long periods. A high contrast ratio creates a more balanced image, making it easier on the eyes.
4. Static Contrast Ratio vs Dynamic Contrast Ratio
Contrast is a key parameter when purchasing LED screens, but many people may be confused by the terms “dynamic contrast” and “static contrast”. Although they are both used to describe the contrast performance of the display, but the actual meaning and measurement are very different. Here are the differences in detail:
4.1 Definition
4.1.1 Static Contrast Ratio (SCR)
Static Contrast is the ratio of brightness between the brightest part (white) and the darkest part (black) of the display in the same picture. It reflects the contrast performance of the display at a fixed brightness.
Formula: Static Contrast Ratio = Maximum Brightness / Minimum Brightness
Example: If the maximum brightness of the screen is 500 nits and the minimum brightness is 0.5 nits, then the static contrast is 1000:1.
4.1.2 Dynamic Contrast Ratio (DCR)
Dynamic Contrast is the ratio between the maximum and minimum brightness of a display in different scenarios, achieved by adjusting the backlight or brightness. It is usually a dynamically changing value, depending on the display’s brightness adjustment technique.
Example: If the display is 1000 nits bright in a bright scene and 0.1 nits bright in a dark scene, then the dynamic contrast ratio is 10000:1.

4.2 Testing Methods
4.2.1 Static Contrast Ratio
Static contrast is measured in the same image, usually using a test pattern (e.g., a black and white checkerboard grid) to evaluate the brightness and blackness performance of a display. This method is closer to actual usage scenarios.
4.2.2 Dynamic Contrast Ratio
Dynamic contrast is calculated by measuring the maximum and minimum brightness of a display at different times. It depends on the display’s backlight adjustment technology, such as reducing the backlight brightness when displaying a dark scene and increasing the backlight brightness when displaying a bright scene.
4.3 Different Practical Meaning
4.3.1 Static Contrast Ratio
Because it measures the contrast ability under the same screen, static contrast ratio is a truer reflection of the display’s day-to-day performance. Static contrast is a more reliable parameter than dynamic contrast ratio.
4.3.2 Dynamic Contrast Ratio
Dynamic contrast ratio is usually much higher than static contrast ratio, but it does not necessarily reflect the picture quality in real use. It relies on backlight adjustment, so it may not provide a significant picture quality improvement when displaying complex images.
4.4 Application
Static contrast ratio is suitable for professional design, video post-production, or other places that needs stable image quality. Dynamic contrast ratio will fit on scenes that require a high contrast ratio such as outdoor LED billboards and HDR video play.
5. Contrast Ratio of LED, LCD, OLED, QLED Displays
The display contrast ratio varies significantly across different display technologies due to the inherent differences in how they produce light and manage black levels. Here’s a comparison of the contrast ratios typically associated with different display technologies:
5.1 LED Displays
Display Contrast Ratio Range: usually 3000:1 to 10000:1 or even higher.
Technical Principle: LED display consists of countless self-luminous LED beads, and each pixel can control the brightness and color independently.
Contrast Performance:
Pros: Excellent black performance, as the beads can be turned off completely to achieve true black.
Cons: Higher cost, higher power consumption, suitable for high-end application scenarios (e.g. outdoor advertising, stage background).
5.2 LCD Displays
Display Contrast Ratio Range: Typically 1000:1 to 3000:1 (static contrast ratio), with dynamic contrast ratios up to millions of:1.
Technical Principle: LCD relies on a backlight source (e.g. LED) to emit light and control the passage of light through liquid crystal molecules to form an image.
Contrast Performance:
Pros: Low cost, mature technology, suitable for most daily use scenarios.
Cons: Poor black performance, as the backlight cannot be completely turned off, resulting in blacks that look grayish.
5.3 OLED Displays
Display Contrast Range: Theoretically close to infinite:1 (as black can be turned off completely).
Technical Principle: Each pixel consists of an OLED light bead that is self-illuminated by organic material, allowing independent control of brightness and color.
Contrast Performance:
Pros: perfect black performance, vibrant colors, fast response time, suitable for high-end TVs and mobile devices.
Cons: High cost, risk of screen burn-in, brightness is usually lower than LED display.
5.4 QLED Displays
Screen Contrast Ratio Range: Typically 3000:1 to 7000:1 (static contrast ratio).
Technical Principle: Adds a quantum dot layer on top of the LCD to enhance color performance and brightness.
Contrast Performance:
Pros: Vivid colors and high brightness for bright environments.
Cons: Black performance is not as good as OLED as it still relies on backlight.
6. 1000:1 vs 3000:1 vs 5000:1 LED Screen Contrast Ratio
When comparing display contrast ratios like 1000:1, 3000:1, and 5000:1, it’s important to understand how these numbers impact the visual experience and which one might be best suited for your needs. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
6.1 What Does Contrast Ratio Mean?
These screen contrast ratios mean the brightest white is 1000/3000/5000 times brighter than the darkest black. The higher the display contrast ratio, the greater the difference between light and dark areas, resulting in more vivid and detailed images.
6.2 Visual Experience Comparison
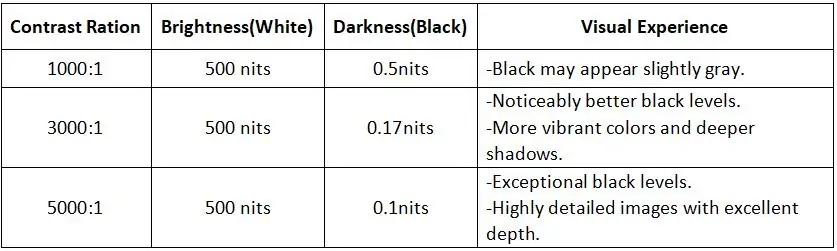
6.3 Key Difference
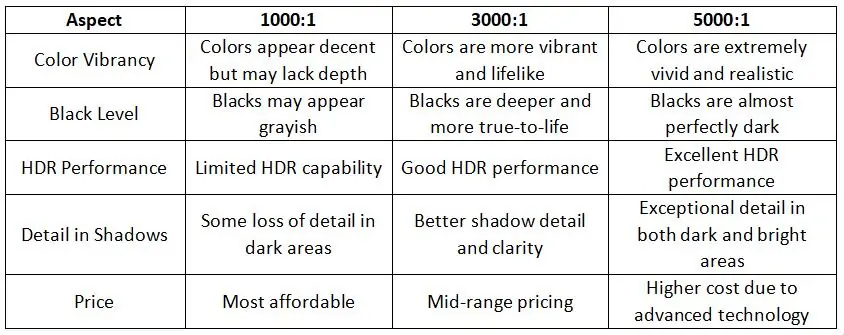
6.4 Real-World Application
1000:1 Contrast Ratio: Suitable for everyday tasks like browsing, streaming, and office work.
3000:1 Contrast Ratio: Great for immersive gaming, movie watching, and creative work.
5000:1 Contrast Ratio: Ideal for professional environments where color accuracy and detail are paramount, such as graphic design, video editing, and luxury home theaters.
7. What Factors Influence Screen Contrast Ratio?
Many factors affect the screen contrast ratio, including display technology, ambient light, and screen characteristics.
7.1 Display Technology
LCD screens rely on backlighting, have a low contrast ratio, and blacks do not appear deep enough. OLED screens have self-illuminated pixels that completely turn off black pixels and have extremely high contrast. The contrast ratio of LED displays depends on the quality of LED and driving technology, high-end products usually have a higher screen contrast ratio.
7.2 Display Processing
Too high a brightness setting will gray out blacks and reduce contrast; a proper brightness setting will improve contrast. Color calibration ensures display accuracy and prevents color deviations from affecting display contrast ratio. High Dynamic Range (HDR) content better demonstrates high contrast.
7.3 Screen Treatment and Features
Anti-reflective coating reduces ambient light reflection and improves contrast ratio. Matte screen scatters light and reduces reflections; Mirror screen reflects significantly in bright light and reduces contrast. High resolution and pixel density make images more detailed, indirectly improving contrast perception.
7.4 Environment and Screen Inner Structure
Strong ambient light reduces the black performance of the screen and affects display contrast ratio. In dark environments, contrast is usually higher. High-quality driver circuits and signal processing technologies provide more precise control of brightness and color and enhance contrast.
8. How to Improve LED Display Contrast Ratio?
Improving the contrast ratio of LED displays can be started with hardware optimization, software adjustment and environmental control. The following are some specific measures:
8.1 Hardware Optimization
High-Quality LED Module: Reduce reflections by choosing LED modules with higher raw contrast, such as LED beads with black masks.
Improve Packaging Technology: Adopt COB (Chip on Board), flip chip technology or other packing technology to reduce light scattering and improve contrast.
Local Dimming: Local dimming technology is introduced into the LED display to dynamically adjust the brightness of different areas, making the darker parts darker and the brighter parts brighter.
Optimized Optical Design: Use high-contrast optical lens to reduce the halo effect. Optimize LED alignment and spacing to avoid light overflow.
8.2 Software Adjustment
Color Calibration: Use professional calibration tools or software to regularly calibrate the color and brightness of the display to ensure accurate representation of black and white.
Dynamic Contrast Adjustment: Dynamically adjust the brightness and contrast of the screen through the software algorithm to adapt to the needs of different scenes.
HDR Support: Optimize picture details with HDR algorithms to make dark and bright areas more distinct.
8.3 Environment Control
Reduce Ambient Light Interference: Choose an LED display with an anti-reflection coating or matte surface treatment. In strong light environments, use a light shield or adjust the display angle to reduce ambient light reflection.
Control Ambient Brightness: Avoid installing the display near direct light or strong light sources. Using LED displays in a dark environment can significantly improve contrast perception.
8.4 Content Optimization
Using High Contrast Content: Play optimized high-contrast content to take full advantage of the display’s performance. Avoid using low-contrast or grayed-out images.
Adjusting Content Brightness: Adjust the content brightness according to the ambient light to ensure a clear picture with a moderate screen contrast ratio.
8.5 Maintenance and Optimization
Regular Cleaning: Dust and dirt will reduce the contrast of the LED display, clean the surface regularly to maintain the LED screen.
Check the Hardware Status: Regularly check the LED beads and driving circuits to ensure brightness and color consistency. Replace aged or damaged LED modules to avoid affecting the overall display contrast ratio.
9. How to Choose the Best Contrast Ratio?
Choosing the best contrast ratio for your LED display depends on several factors, including the intended use, viewing environment, and the type of content you plan to display. Here’s a guide to help you determine the best screen contrast ratio for your needs:
9.1 Consider the Display’s Intended Use
For Home Entertainment (Movies and TV Shows): OLED displays, with their infinite contrast ratios, are ideal for this purpose, but Mini-LED or QLED displays with high contrast ratios (around 10,000:1 or more) also perform well.
For Gaming: A high contrast ratio improves shadow details and the overall gaming experience. A contrast ratio of at least 5,000:1 is recommended for gaming displays.
For Professional or Business Use (Presentations, Work): In these environments, color accuracy and sharpness are more important than extreme contrast. A moderate contrast ratio of 1,000:1 to 3,000:1 should be sufficient for standard office tasks.
For Outdoor or Public Displays: Contrast ratio is important for visibility, especially in direct sunlight. An IP-rated display with a high contrast ratio (around 3,000:1) ensures better readability.
9.2 Evaluate the Viewing Environment
Bright Environments: If you’re placing your display in a bright room or near windows, prioritize a higher contrast ratio, possibly around 5,000:1 or better. This ensures the image is still visible even under challenging lighting conditions.
Dark Environments: For home theaters or other settings where the display will be used in a dark environment, look for a high contrast ratio (10,000:1 or more), preferably with OLED technology, to achieve true black levels and excellent detail in dark scenes.
9.3 Look for Technologies with True Black Capabilities
LCD/LED with Local Dimming: They allow specific areas of the screen to darken, which helps to achieve better black levels. The display contrast ratio is around 3000:1 to 10,000:1.
OLED: OLED displays provide the best contrast ratio because they can turn individual pixels off, producing true blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This is ideal for applications where color depth and image quality are paramount.
Mini-LED: If you want the best of both worlds—improved contrast and brightness—Mini-LED technology can deliver excellent contrast ratios (up to 50,000:1 or more) while still providing excellent brightness, making it suitable for bright environments.
QLED: While not as perfect as OLED for black levels, QLED offers excellent color reproduction and contrast ratios (often around 10,000:1), making it a strong choice for bright rooms or when you need vibrant, eye-catching visuals.
9.4 Budget Consideration
Displays with higher contrast ratio (e.g., OLED or Mini-LED) tend to be more expensive. Balance your budget with your needs—don’t overpay for contrast ratio if you don’t need it.
9.5 Key Recommendation
- For Most Users: A contrast ratio of 1000:1 to 3000:1 is sufficient.
- For Enthusiasts/Gamers: Look for 3000:1 or higher, or consider OLED/Mini-LED.
- For Professionals: Prioritize color accuracy and static contrast ratio over dynamic contrast.
10. FAQs
1. Is 1000000:1 a Good Display Contrast Ratio?
Yes, a 1,000,000:1 contrast ratio is excellent, but it’s likely a dynamic contrast ratio, which measures the display’s ability to adjust brightness in different scenes. For true image quality, focus on the static contrast ratio (typically 1000:1 to 3000:1 for most displays).
2. What is the Lowest Contrast Ratio?
The lowest usable contrast ratio for most displays is around 200:1 to 300:1. Below this, images may appear flat, with the poor distinction between dark and light areas, making it hard to see details.
3. Is High Contrast Good for Eyes?
High contrast is not necessarily good for the eyes. While it can make images appear sharper and more vivid, excessively high contrast, especially in poor lighting conditions. It’s important to balance contrast with ambient lighting and adjust settings to a comfortable level for prolonged use.
4. Should Contrast be Higher than Brightness?
Yes, generally, contrast should be higher than brightness for optimal viewing. Higher contrast ensures better distinction between dark and light areas, enhancing image clarity and detail. However, both settings should be balanced to avoid eye strain—excessive brightness with low contrast can wash out images, while too much contrast with low brightness can make details hard to see.
11. Summary
We hope that through the analysis in this article, you can better understand the importance of contrast ratio and make a more informed decision when choosing an LED video wall to enjoy better visual enjoyment!
In short, contrast ratio is more than just a number in a display’s technical specifications, it directly affects the vividness and detail of an image. Whether for daily office work, entertainment viewing or professional design, choosing the right contrast ratio can significantly enhance your visual experience.






























